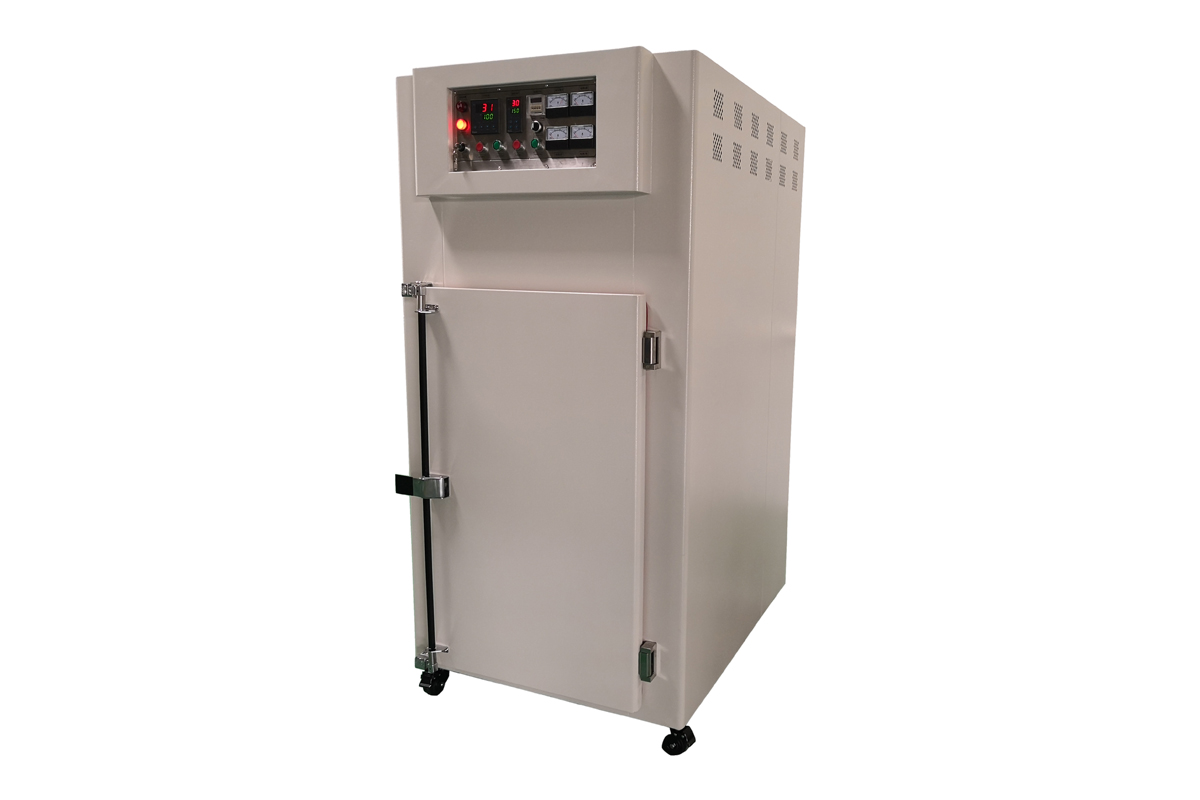
Industrial Ovens play a critical role in the heat treatment processes that are essential for enhancing the mechanical properties, durability, and performance of materials across various industries. Heat treatment processes such as annealing, hardening, curing, and tempering are used to modify the physical and chemical characteristics of metals, plastics, and other materials to meet specific engineering requirements.

1. Annealing: Softening Materials for Better Formability
Annealing is a heat treatment process that involves heating a material, typically a metal, to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. This process helps to reduce hardness, relieve internal stresses, and improve the material's ductility and formability, making it easier to work with in subsequent stages of production.
Industrial Ovens used for annealing must be capable of maintaining a consistent, uniform temperature over long periods. The ovens are equipped with precise temperature control systems to heat the material to the required temperature (often between 300°C and 900°C depending on the material), followed by a controlled cooling phase. This ensures that the material has the desired mechanical properties, such as increased flexibility and reduced brittleness, making it ideal for applications like metal forming, machining, or welding.
How Industrial Ovens Improve Material Properties in Annealing:
Uniform heating: Ensures even treatment across all areas of the material.
Stress relief: Reduces internal stresses, preventing distortion or cracking.
Improved ductility: Increases the material's ability to be shaped or bent without breaking.
2. Hardening: Increasing Strength and Durability
Hardening is a heat treatment process used to increase the hardness and strength of metals, particularly steel. The process involves heating the material to a high temperature, followed by rapid cooling, often in water or oil, known as quenching. This process causes the metal's structure to change, increasing its hardness and making it more resistant to wear and deformation.
Industrial Ovens used for hardening are designed to provide precise control over the heating process, ensuring that the material reaches the required temperature for the transformation to take place. Additionally, the oven must be equipped to handle the rapid transition to the quenching stage, which often involves controlled cooling chambers adjacent to the heating system.
How Industrial Ovens Improve Material Properties in Hardening:
Increased hardness: The rapid cooling traps carbon in the steel, making it harder.
Enhanced strength: Hardening increases the tensile strength of the material, making it more suitable for high-stress applications such as automotive components and tools.
Wear resistance: Hardening improves the material’s resistance to wear, reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of products.
3. Curing: Enhancing Chemical and Physical Properties of Polymers
Curing is a heat treatment process commonly used in the production of polymers, adhesives, coatings, and paints. The goal of curing is to harden or solidify the material, which is typically in a liquid or semi-solid form before treatment. By heating the material to a specific temperature, curing promotes chemical reactions that form cross-links in the polymer chains, creating a stronger and more durable product.
In industries like automotive manufacturing, construction, and electronics, curing ovens are used to treat everything from paint coatings to rubber components. These industrial ovens provide precise temperature control to ensure uniform curing and avoid defects like uneven curing or insufficient cross-linking.
How Industrial Ovens Improve Material Properties in Curing:
Increased strength: Curing forms a stronger molecular structure, enhancing the material's mechanical properties.
Improved durability: Cured materials exhibit enhanced resistance to heat, chemicals, and wear, increasing their service life.
Uniformity: A uniform curing process ensures consistent quality, which is essential in large-scale manufacturing.
4. Tempering: Reducing Brittleness After Hardening
Tempering is typically performed after hardening to reduce the brittleness of hardened metals, especially steel. After a material has undergone the hardening process, it may become too brittle and prone to cracking under stress. Tempering involves reheating the hardened material to a lower temperature (usually between 150°C and 650°C) and then cooling it slowly. This process helps to reduce the hardness slightly while improving toughness, making the material less likely to fracture under load.
Industrial ovens used for tempering must be capable of reaching and maintaining precise temperatures over a wide range, as the tempering process requires fine control to achieve the desired balance between hardness and toughness.
How Industrial Ovens Improve Material Properties in Tempering:
Increased toughness: Tempering restores some of the ductility lost during hardening, preventing cracks and fractures.
Enhanced workability: The material becomes easier to machine, weld, or shape without cracking.
Improved resistance to fatigue: Tempered materials are less likely to fail under cyclic stress, making them ideal for structural components in automotive, aerospace, and machinery industries.
The Benefits of Industrial Ovens in Heat Treatment
Industrial ovens are designed to deliver precise, uniform, and controlled heat treatment processes. The role of these ovens in enhancing material properties is crucial for improving the strength, durability, and performance of components used in a wide range of industries. Key benefits include:
Improved production quality: By providing consistent and uniform temperature profiles, industrial ovens ensure that every part meets the required specifications.
Increased efficiency: Industrial ovens are optimized for rapid heating and cooling cycles, improving overall production speed and reducing downtime.
Cost-effectiveness: Well-designed ovens reduce energy consumption by maintaining precise temperature control and minimizing heat loss, leading to lower operational costs.
Industrial ovens are indispensable in heat treatment processes such as annealing, hardening, curing, and tempering. They provide the necessary conditions to enhance material properties, such as hardness, strength, toughness, and durability, making them vital in sectors like automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and electronics. By leveraging advanced technology and precise temperature control, these ovens ensure high-quality production, optimized efficiency, and improved performance of materials in critical applications. As industries continue to demand more advanced and reliable materials, the role of industrial ovens in heat treatment processes will only become more central in ensuring quality and innovation in manufacturing.