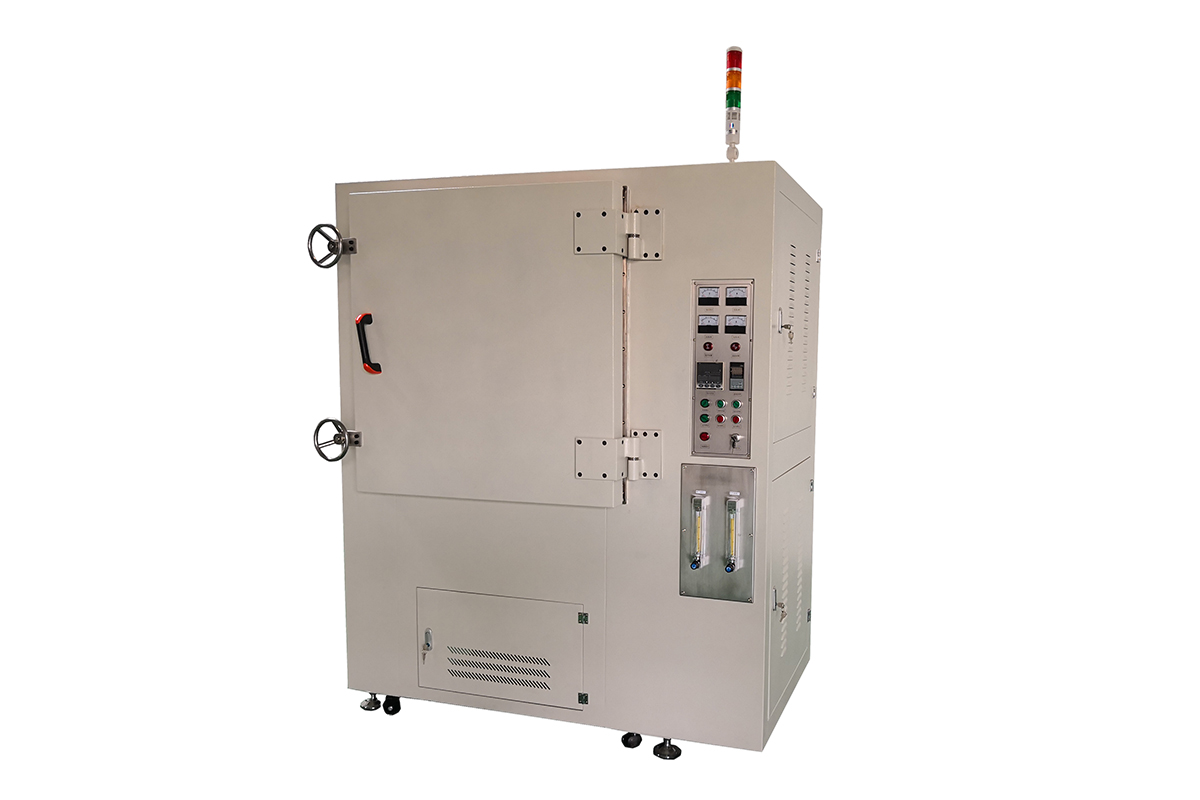
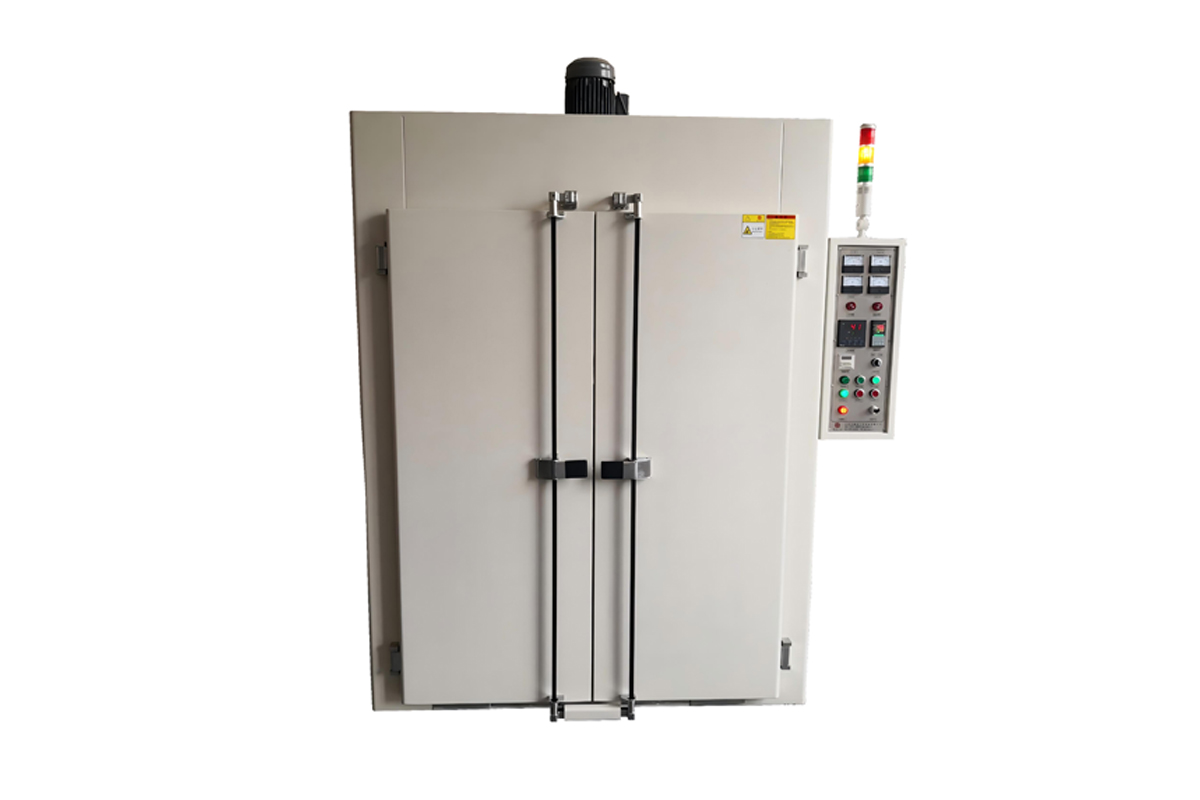
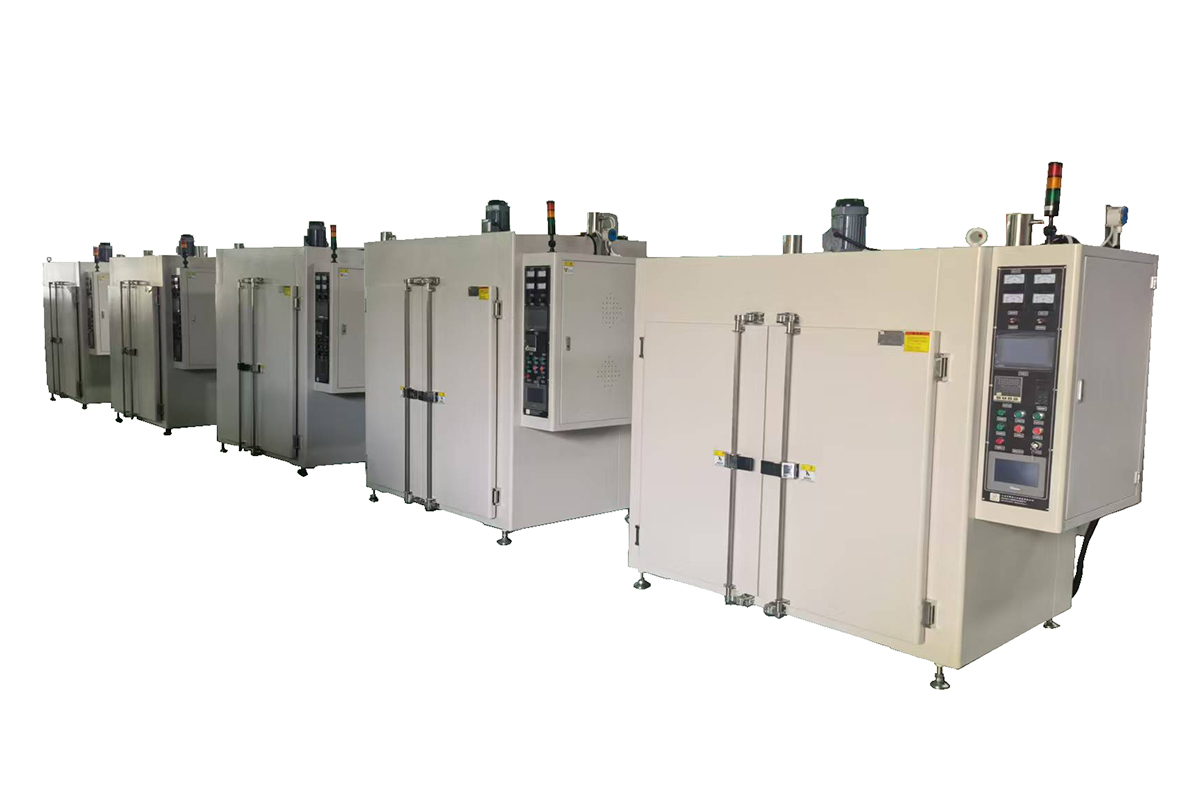
A High Temperature Oven is a specialized equipment designed for heating, baking, drying, and heat treatment processes that require high-temperature conditions. It is essential in a wide range of industrial and laboratory applications, especially for materials processing such as metal heat treatment, ceramic sintering, plastic aging tests, and other precision manufacturing processes.
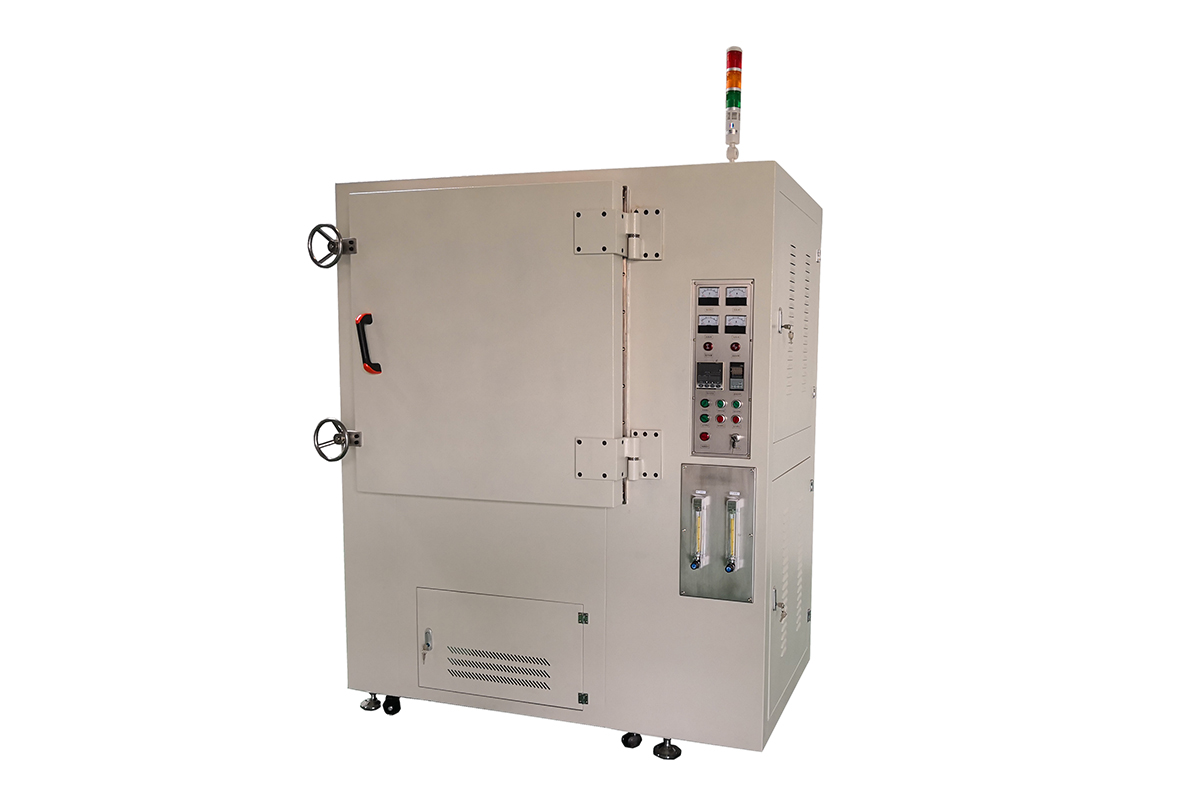

Key Features
1.High Temperature Resistance: High-temperature Ovens typically handle temperature ranges from 200°C to 1600°C (or even higher), making them suitable for a wide variety of heat treatment processes.
2.Precise Temperature Control: Equipped with advanced temperature control systems, these ovens ensure accurate temperature settings and stable performance, with temperature deviations typically within ±1°C.
3.Even Heating: High-temperature ovens feature powerful air circulation systems that ensure uniform temperature distribution throughout the chamber, preventing hot spots or cold zones and delivering consistent results.
4.Energy Efficiency: These ovens are designed with high-performance insulation materials and intelligent temperature control systems to minimize energy consumption while maintaining heating efficiency.
5.Safety Features: High-temperature ovens are built with multiple safety features such as overheat protection, door safety switches, and alarm systems to ensure safe operation even under extreme temperature conditions.
Technical Specifications of a High Temperature Oven:
| Specification | Details |
|---|
| Temperature Range | 200°C ~ 1600°C (depending on model) |
| Heating Method | Electric heating with high-quality heating elements and advanced air circulation system |
| Temperature Accuracy | ±1°C |
| Internal Dimensions | Common capacities: 400L, 600L, 1000L, etc. |
| Control System | Digital temperature control, touchscreen interface, PLC programmable control |
| Exterior Material | High-temperature steel or stainless steel (corrosion and heat-resistant) |
| Safety Features | Over-temperature protection, overheat alarms, electrical leakage protection, automatic power-off function |
| Power Supply | 220V / 380V (depending on model and regional requirements) |
| Air Circulation System | Forced air circulation for uniform heating |
| Max. Ambient Temperature | Typically up to 50°C (depending on model) |
| Insulation | High-performance thermal insulation to reduce energy consumption |
| Noise Level | ≤ 60 dB (depending on model) |
Main Functions
1.Drying and Dehydration: Suitable for drying a variety of materials, especially electronic components, metal parts, and ceramics.
2.Heat Treatment and Aging Tests: Used for heat treating metals, plastics, rubber, and other materials, simulating the long-term effects of high temperatures to test durability and performance.
3.Sintering and Melting: Essential for the sintering of ceramics and metals, assisting in the formation of stronger materials under high heat.
4.Research and Development: Commonly used in laboratories for high-temperature tests and material research, ensuring that processes are carried out under controlled conditions.
Applications
1.Metal Industry: Used for processes like metal heat treatment, hardening, annealing, and tempering.
2.Electronics Manufacturing: Applied in drying and aging tests of electronic components, such as circuit boards (PCBs).
3.Ceramics and Glass Industry: Crucial for sintering ceramics and melting glass materials.
4.Automotive Industry: Testing coatings, rubber, and plastic parts under high-temperature conditions.
5.Laboratories: Widely used in chemical, physical, and material science research for high-temperature testing and data collection.
6.Plastic and Rubber Industry: For aging tests and processing plastic and rubber products under extreme conditions.